Have you ever heard of the Bitcoin halving? Most people don’t understand how Bitcoin works well enough for the halving to make immediate sense to them, but don’t worry. That’s what this quick Bitcoin halving breakdown is for.

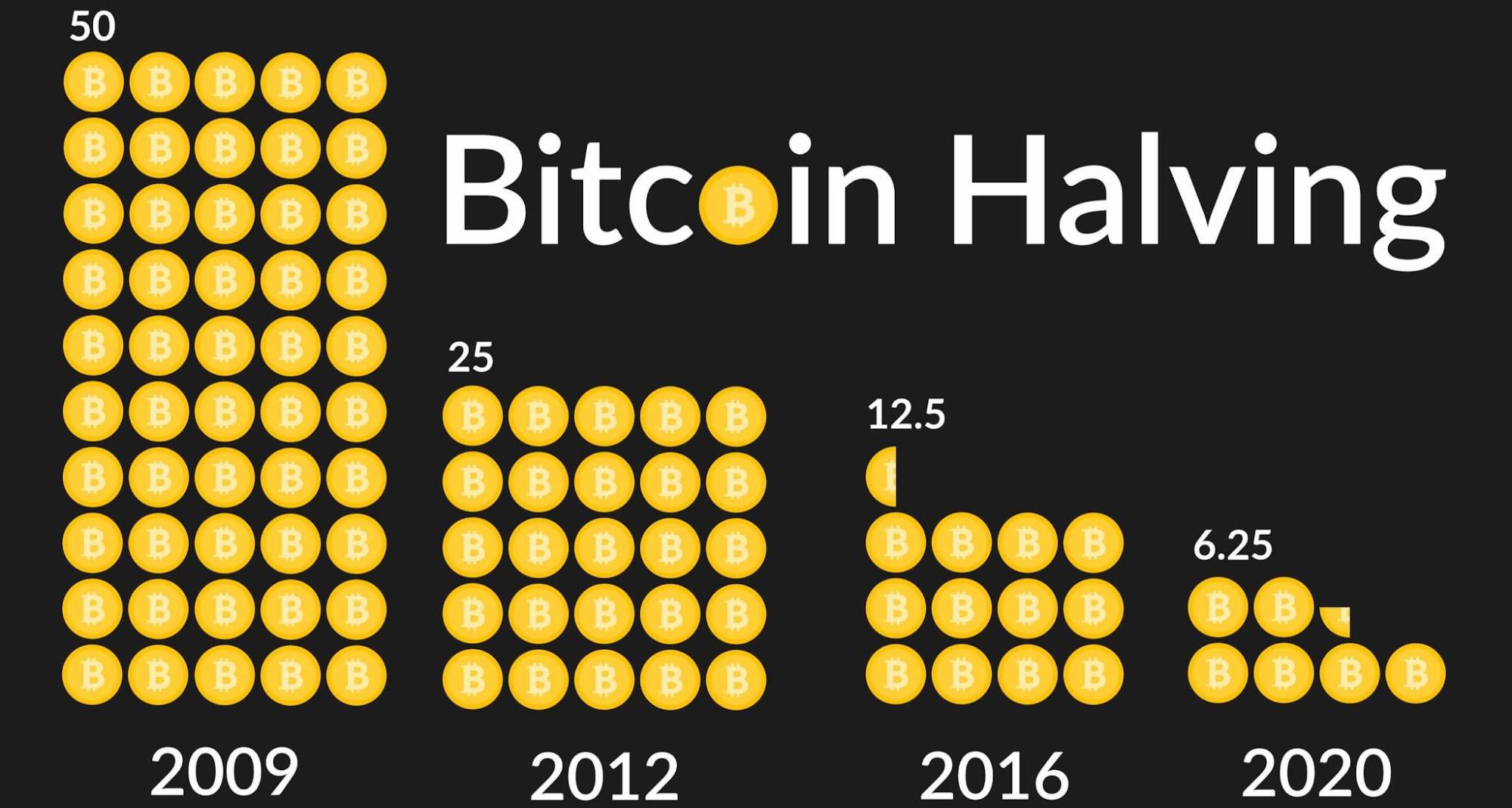
You may have heard that the total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million. Today, there are around under 19.6 million coins in circulation. New Bitcoins are created when Bitcoin miners, who maintain the blockchain network, verify transactions and gain block rewards. Every time 210,000 blocks are mined, the block reward for Bitcoin miners is cut in half. Here’s what that means…
Deflationary characteristics
The reason Satoshi Nakamoto created a total supply limit for Bitcoin is to keep it deflationary, in contrast with fiat currencies like the dollar, which are intentionally devalued. There is some argument about whether Bitcoin will stay as deflationary as it was intended to be, but so far in its history, it has.
When the block reward is cut in half, the rate of inflation created by increasing total supply is slowed, theoretically driving up the price. While Bitcoin has continued to be very volatile in the short term, with every halving, the long-term value trajectory has certainly been going up.
The last Bitcoin halving
The last Bitcoin halving happened on May 11, 2020, when the block reward was cut from 12.5 bitcoins per block to 6.25. Even though the rewards are reduced roughly every four years, Bitcoin miners are still incentivized to mine because the value of the currency has continued to increase.
The last block will be mined around 2140
Since the Bitcoin halving happens every 210,000 blocks instead of at a certain time interval, we don’t know exactly when the last block will be mined, but based on the transaction rate through history, the final Bitcoin will be mined around the year 2140.
Transaction fees will replace block rewards

So, what happens when the last block is mined? Why will Bitcoin miners still want to maintain the blockchain? The answer is transaction fees. Even though new Bitcoins won’t be created after the 21 million total is reached, Bitcoin miners will receive rewards in the form of fees for approving transactions that are added to the blockchain.
Mined Bitcoins are harder to trace
Hopefully, if you have crypto, you know that it’s not completely anonymous. Especially today with many centralized fiat on-off ramps requiring KYC information, it’s fairly easy to track who owns what Bitcoins. One reason some people become Bitcoin miners is because if you obtain newly created Bitcoins instead of trading for them, it’s easier to avoid identifying information being attached to them.
Conclusion
These are some quick need-to-know facts about the Bitcoin halving and why Bitcoin miners are so eager to maintain the blockchain. At the time of this writing, one block reward is worth around $263,941.88. Plus, if Bitcoin maintains its deflationary properties, that value will only go up. That’s a pretty good reward if you ask me.
About the Author

Emily Weber
About Decentral Publishing
Decentral Publishing is dedicated to producing content through our blog, eBooks, and docu-series to help our readers deepen their knowledge of cryptocurrency and related topics. Do you have a fresh perspective or any other topics worth discussing? Keep the conversation going with us online at: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.


