Many newbies to the crypto world use Ethereum and Ether interchangeably to refer to the Ether (ETH) cryptocurrency (I’m definitely guilty of that). But the two are actually entirely different. Ethereum is the technology company behind the coin Ether. But what exactly is Ether’s role in the Ethereum network?
What is the Ether (ETH) coin?
 ETH is the Ethereum value token (aka cryptocurrency) used within the network. Unlike Bitcoin, its purpose isn’t to become a replacement for fiat money. Instead, it’s mainly used as an incentive to drive the Ethereum network and keep it running.
ETH is the Ethereum value token (aka cryptocurrency) used within the network. Unlike Bitcoin, its purpose isn’t to become a replacement for fiat money. Instead, it’s mainly used as an incentive to drive the Ethereum network and keep it running.
Ethereum is an open platform where anyone can create decentralized applications (dApps) by coding a smart contract with Ethereum’s coding language, Solidity.
Let’s take a closer look at the purpose of ETH and how it was created to better understand this concept and how it works.
The purpose of ETH
Ether plays several roles in the Ethereum network:
- Users making a transaction on Ethereum must pay a fee of ETH. This fee incentivizes the blockchain’s network of nodes to process, verify, and add the transaction to the blockchain.
- Users who create new smart contracts or dApps must pay ETH to deploy them to the network. Since each contract is deployed to the network and takes up computing power, this fee ensures that the contracts entering the pool are high-quality and have some legitimacy behind them.
- ETH is used as the digital currency within different dApps on the Ethereum network.
- ETH can be used as a store of value; you can invest in it, stake it, use it to pay for goods and services, use it as collateral for a loan, or exchange it for another crypto.
When understanding the role of Ether in the Ethereum network, it’s important to understand the concept of “gas.”
The amount of ETH someone pays for a transaction is determined by how much computational effort it will take to process and execute the transaction (remember that transactions include creating smart contracts and dApps).
Gas is the unit of measurement that measures how much computational power a transaction will use. Users of the Ethereum network refer to transaction fees as “gas,” which are paid in ETH. Gas keeps the platform running, the same way gas in a car keeps a car running.
How ETH is created
Unlike Bitcoin, the Ethereum value token has no supply cap, which means an infinite amount of it can be created. While no one knows exactly how much ETH will ever be in circulation, it’s suspected that the amount of new ETH able to be created will begin to decrease once Ethereum transitions to Ethereum 2.0 and a proof-of-stake model.
Currently, ETH is mined through a proof-of-work style system, just like Bitcoin. Miners use their computers to verify each transaction before adding it to the blockchain. They do this by solving complex cryptography puzzles. As a reward for this computational work, they receive some ETH.
Ethereum is currently planning to transition away from a proof-of-work system and start using a proof-of-stake system in the coming year. When this happens, ETH will be earned by crypto staking. Users must have at least 32 ETH in order to participate in staking.
There are a few different ways you can get ETH that is already in circulation:
- Buy it with fiat currency: use fiat currency to purchase some ETH, whether you plan to hang on to it as an investment, use it as collateral for a loan, or pay for goods and services. You can buy ETH on any major crypto exchange.
- Exchange another crypto for Ether: for example, you can trade your Bitcoin for Ethereum. This can be done on any crypto exchange that allows for a BTC/ETH pairing.
- Give or receive it in a transaction: receive crypto as part of a transaction on the Ethereum network.
Keep in mind that you will need an Ethereum crypto wallet in order to keep and use your ETH on the Ethereum network.
Key milestones in Ether’s history
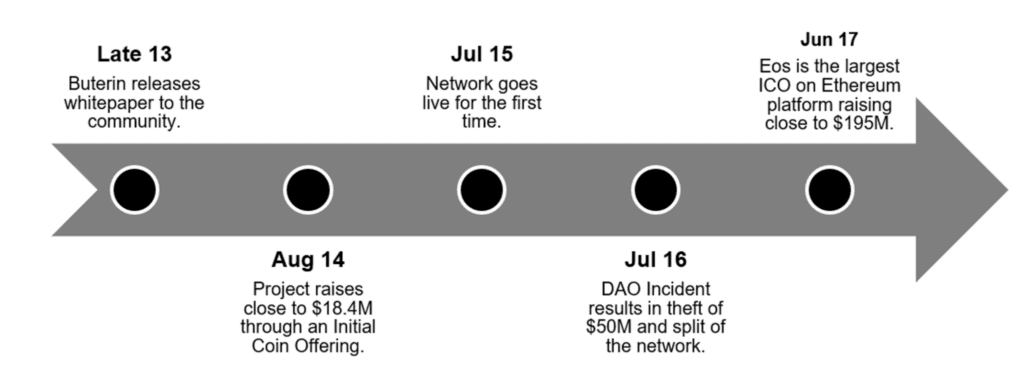 Ether was conceived and described in the original whitepaper for Ethereum, which was written in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin.
Ether was conceived and described in the original whitepaper for Ethereum, which was written in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin.
Since the official launch of Ethereum in 2015, it has been an integral part of the company’s vision for a decentralized system.
In May 2021, the value of ETH grew exponentially, to over $4,000 for one ETH, which it remains at currently. In contrast, only a year earlier, the cost of one ETH was $85.
The ways you can use ETH have continued to grow as more decentralized applications are created and the Ethereum network continues to grow. While Ether may not overtake Bitcoin as the number one crypto any time soon, it’s clear that many people see its value.
The future of Ether
 As mentioned above, Ethereum will be moving away from a proof-of-work system in favor of proof-of-stake in its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. This will have big implications for the way ETH is used on the Ethereum network.
As mentioned above, Ethereum will be moving away from a proof-of-work system in favor of proof-of-stake in its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. This will have big implications for the way ETH is used on the Ethereum network.
A proof-of-stake model will mean that ETH plays a crucial role in helping to secure the blockchain. With this system, users need to stake at least 32 ETH in order to participate. This ETH is essentially “locked up” and can’t be traded or spent in any way.
Users will earn rewards in the form of more ETH for keeping their crypto locked up, similar to earning interest in a savings account with your bank. In this way, the Ethereum value token will act as an economic incentive for users to maintain a secure and accurate blockchain.
Staking ETH will help the company scale faster, increase environmental sustainability, and improve security.
About the Author

Jennifer Jones
About Decentral Publishing
Decentral Publishing is dedicated to producing content through our blog, eBooks, and docu-series to help our readers deepen their knowledge of cryptocurrency and related topics. Do you have a fresh perspective or any other topics worth discussing? Keep the conversation going with us online at: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.


